Lecture 7.1
Washington Consensus Reforms
Emmanuel Teitelbaum
The Washington Consensus
10 Policy Prescriptions
- Fiscal discipline
- Public expenditure (investment vs consumption)
- Tax reform (expand tax base, cut marginal rates)
- Financial liberalization
- Competitive exchange rates
- Trade liberalization
- Foreign direct investment (remove barriers)
- Privatization of state-owned enterprises
- Deregulation of markets
- Secure property rights
Economic Crisis
Elements of an Economic Crisis
- Recession
- Low or negative growth rates
- High unemployment
- Hyperinflation & shortages
- Government prints money to cover debts
- Hoarding
- Balance of payments crisis
- Sudden stops or reversals of capital inflows
- Debt crisis
- Proliferation of public debt relative to GDP
- Financial crisis
- Assets bubbles
Causes of Crisis (Neoliberal Diagnosis)
- “Bloated” public sector
- Inefficient/wasteful
- Crowds out private sector investment
- Corruption
- Deters investment generally
- Over-regulation of private sector
- Impedes expansion of formal sector
- Government spending and debt
- Drives inflation
Crisis in Eastern Europe
Economic Organization Under Communism
- Centralized planning
- Bureaucratically established quotas and targets
- No market dynamics of supply and demand
- Key economic goals
- Full employment
- State ownership and control
- International isolation/autarchy
Pitfalls of Central Planning
- Information
- No price mechanisms
- Government is not omniscient
- No way to regulate supply and demand
- Barter economy, black markets and shortages
- Perverse incentives
- No profit-maximizing behavior
- Lack of innovation
- Soft budget constraints in public sector: waste, theft, poor quality of goods
Adverse Results
- Widespread theft and embezzlement of state property
- Centralized planning system stops working
- Escalating inflation because counties keep printing money
- Mass shortages of even basic goods

Crisis in India
India’s Economic System
- “Nehruvian” industrial policy rather than central planning
- Import substitution
- Protection of domestic industry
- High tariffs
- Market controls
- ‘License-Quota Raj’
- Dominance of the public sector
- Low quality goods
- Shortages
- Inefficiency
- End result: inflation and decreased trade
1991 Economic Crisis
- Proximate cause: balance of payments (BOP) crisis
- Occurs when the total amount of receipts is less than the amount of total payments
- Causes of crisis in India
- Collapse of Soviet Union (Trade)
- Gulf War (Oil)
- Capital flight, speculative attack on credit, balance of payments and currency crisis
Neoliberal Reforms
Reform #1: Stabilization
- Goal: prevent hyperinflation from escalating out of control
- Austerity regime meant to curb inflation
- Reduce or halt public spending
- Curb public expectations
- Devalue currency
- Raise taxes and government revenue
- Can’t print money to solve the problem
Reform #2: Liberalization
- End price controls, production quotas, reservations, etc.
- Encourage foreign trade and investment
- Reduce tariff barriers
- Lift curbs on foreign direct investment
- Goals
- Attract real money, which is in short supply
- Increase competition and innovation
- Spur investment in industry and high-end services
- Reduce state subsidies (expensive, interfere with market forces)
- Cash, tax breaks, loan guarantees, procurement prices, stock purchases
- Farm, oil, housing, export, etc.
- Financial sector reforms
- Allow private and foreign banks freedom to operate
Reform #3: Privatization
- Selling off of state assets to private actors
- Develop greater efficiency and increase output
- Better managers
- Better incentives
- Create markets and entrepreneurs
- Generate revenue for the state
Reform #4: Structural Adjustment
- Long-term structural reform
- Extending neoliberal reforms
- Reducing government role in economy
- Liberalizing factor markets
- Land, labor, capital
- The ultimate goal is to boost productivity
- Not just removing price controls or privatizing
- Making institutions growth-enhancing
- Industrial policy, investment policy, governance, etc.
Shock Therapy vs. Gradualism
“Shock Therapy”
- Quick moves to stabilize the economy through an evolutionary approach
- Goal of remaking economies quickly
- Internationally-renowned teams experts sent to oversee reforms
- Eastern Europe is a good example
Gradualism
- Step-by-step implementation of reforms
- Put correct political institutions in place before revamping the economy
- Courts, tax inspectors, regulatory agencies, and financial intermediaries
- Advocated by other prominent economists (Joseph Stiglitz) and intellectuals
- India is a good example
- Fast on trade, investment and license quota raj
- Slow on privatization, labor law and other contentious reforms
“Partial Reform Equilibrium”
- Winners of early reforms blocked further progress:
- Benefited from access to legislation and coveted assets
- Created a system in between capitalism and communism where a select few benefitted
- State Capture
- Powerful private interests asset control over both the economy and political decisions
- Think oligarchs!
Businesses Corrupting the State
- Innovative ways of wielding influence
- Buying laws outright
- Running for elected office
- Hiring the relatives of politicians
- Mobilizing their workers to act politically
Effectiveness of Reforms
Transition Progress in Eastern Europe
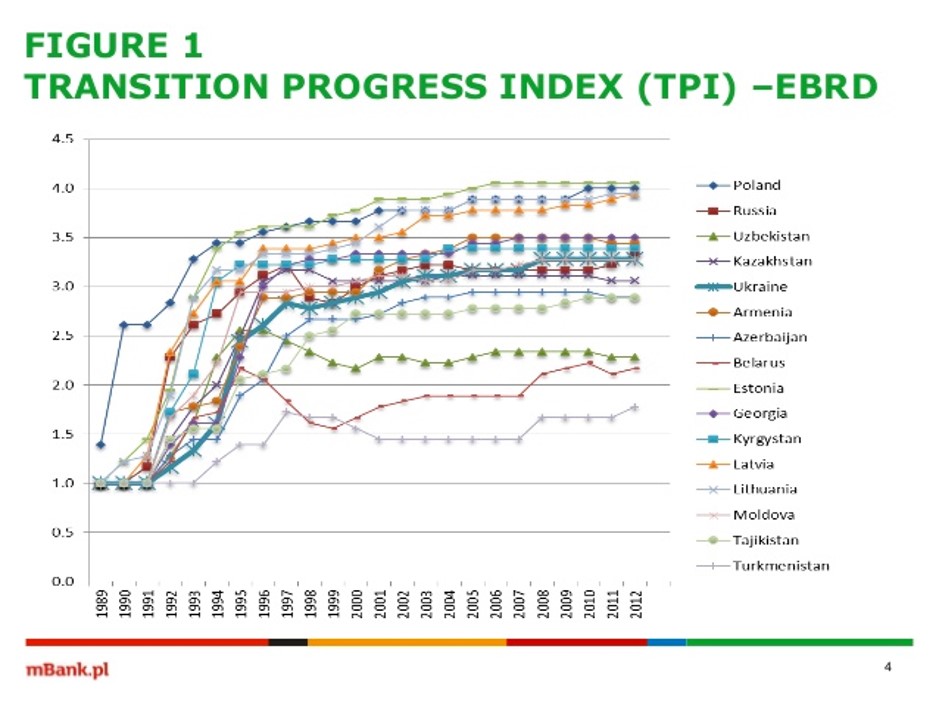
EBRD TPI
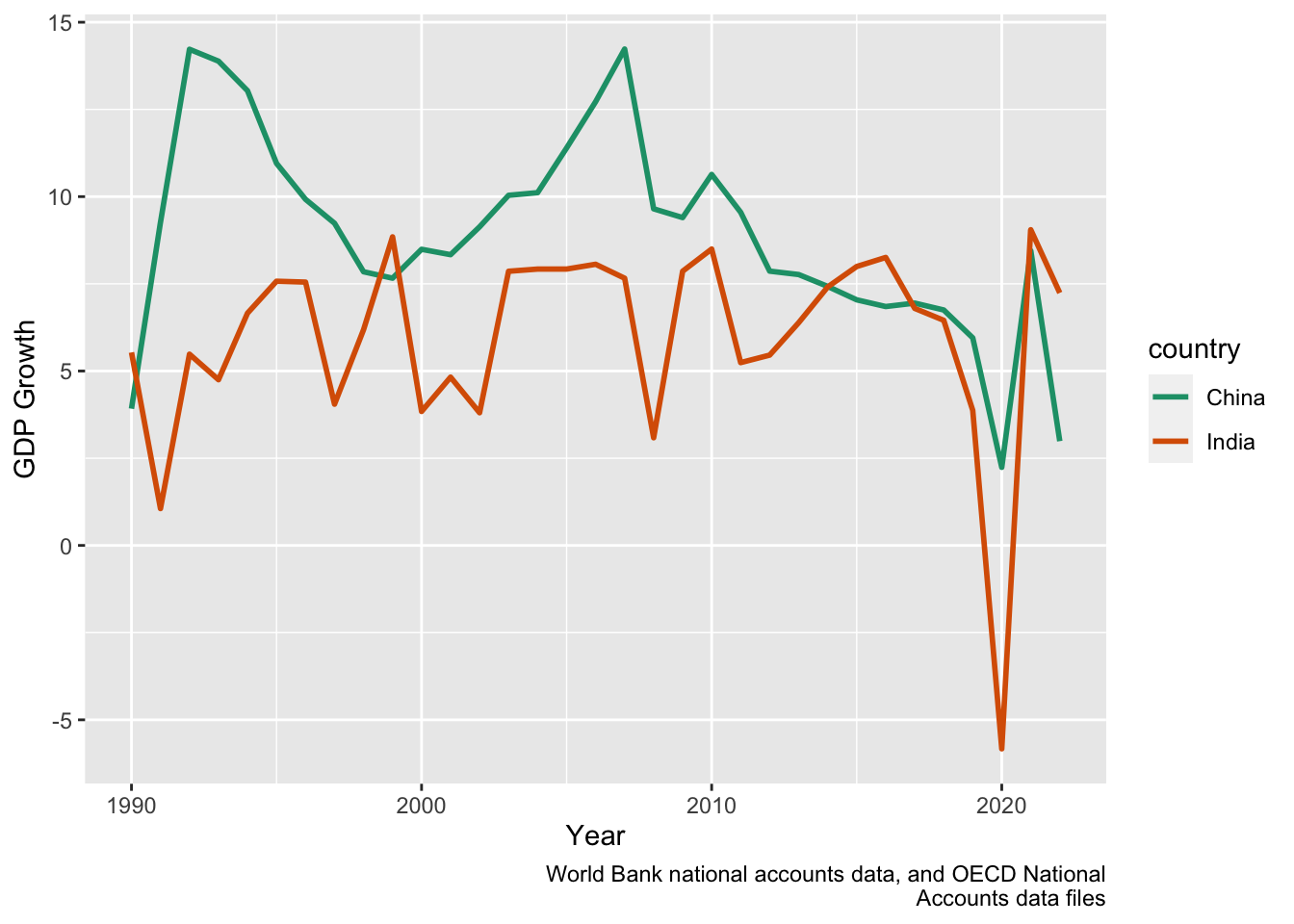
Growth Rates in India and China
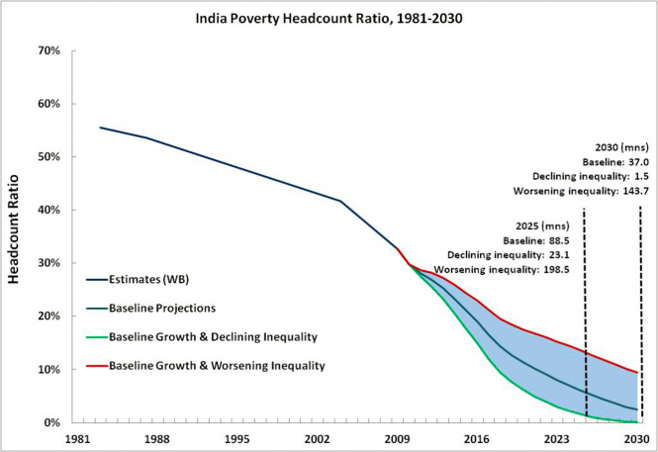
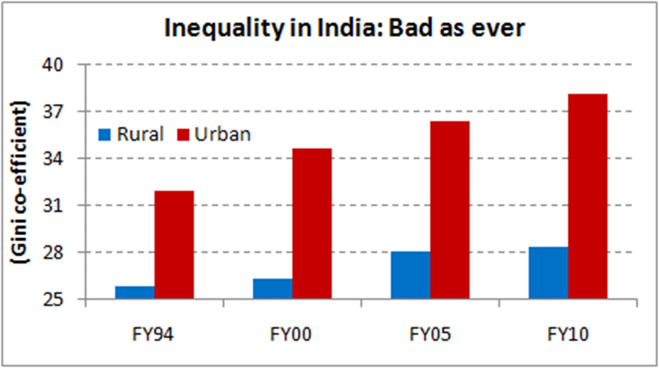
Poverty and Inequality in India
Discussion
Archibong et. al.
- What is the main hypothesis?
- What reforms are they examining in the African context?
- Quantitative analysis
- What are they trying to show?
- Is it convincing
- Case studies, each group take one